

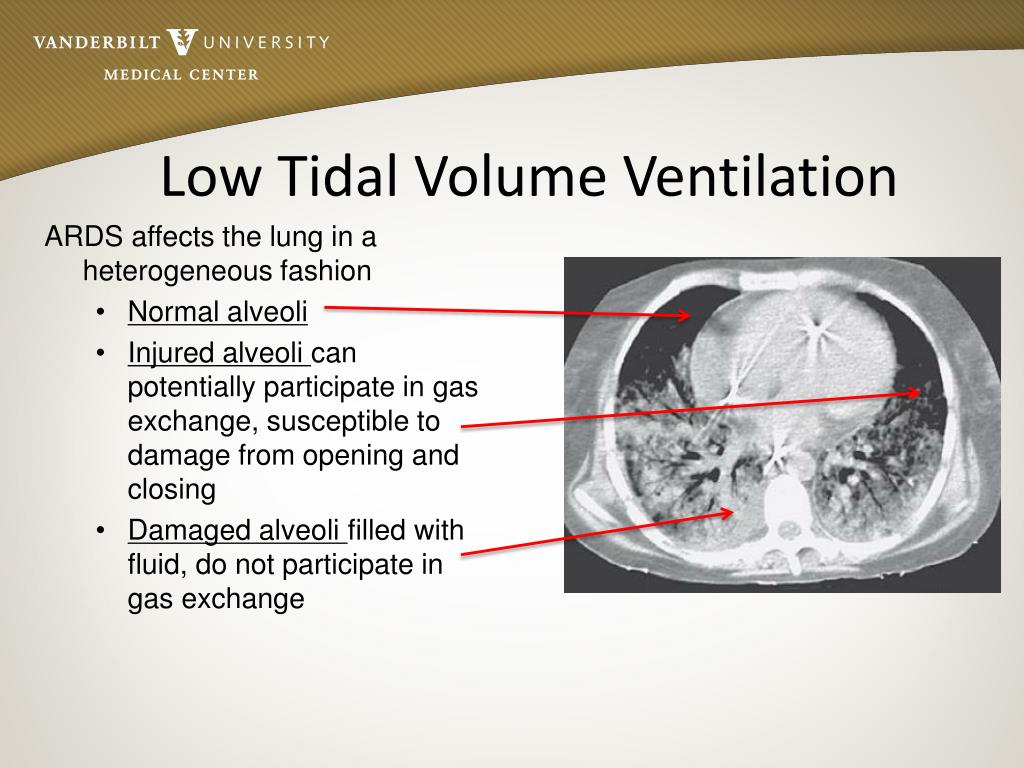
Low tidal volume ventilation, or LTVV, protects lungs from a variety of insults and injuries associated with mechanical ventilation. In addition, the emerging evidence indicates that LTVV is a best practice for all ventilated patients to reduce ventilator-associated harm. However, low tidal volume strategies are probably beneficial in all mechanically ventilated patients, beyond only ARDS patients.Ī low tidal volume strategy has become the standard of care for patients with ARDS as well as the best practice in order to improve outcomes in those patients. More recent studies confirm that LTVV benefits ARDS patients. The 2000 ARDSNet study found a significant benefit for patients with ARDS when using lower tidal volumes (6 cc/kg versus a more traditional tidal volume of 12 cc/kg. Why should we be taking this approach in trying to apply it to our patients? So why should we be using a LTVV strategy?
Predicted body weight and PEEP are the two main components of low tidal volume ventilation. We’ll explain some of the data advocating for positive end-expiratory pressure settings, or PEEP, at or above 5 centimeters of water. The other big component of low tidal volume strategy is the avoidance of the use of ZEEP. It’s not based on their actual body weight, nor even an ideal body weight. Predicted body weight is the key measurement, and is based purely on the patient’s height and their gender. LTVV is an approach that targets tidal volume between 6 and 8 milliliters per kilogram of predicted body weight for patients without acute respiratory distress syndrome or ARDS, and 4 to 6 milliliters per kilogram of predicted body weight for those with ARDS. It targets much lower tidal volumes than those that have been traditionally used while also focusing on the avoidance of zero positive end-expiratory pressure (ZEEP). LTVV is a lung protective strategy that seeks to prevent ventilator-associated lung injury. What is low tidal volume ventilation strategy? Your unit may already be implementing a low tidal volume ventilation strategy to protect your patients’ lungs, or you may need more information to drive the process forward and engage your staff. You may be somewhat familiar with the concept of low tidal volume strategy. Slide 3: What is Low Tidal Volume Ventilation? You will also be able to describe the role of LTVV in the prevention of ventilator-associated events, outline the historical background and scientific evidence supporting the use of LTVV, and recommend evidence-based standards for implementing a LTVV strategy.
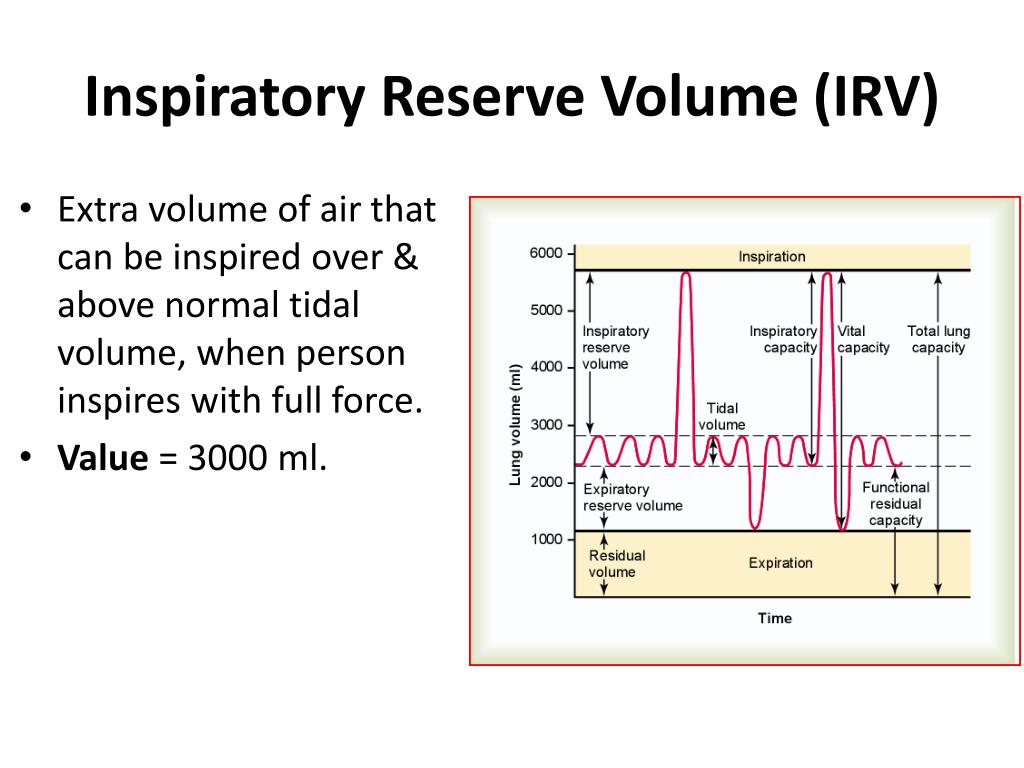
Slide 2: Learning ObjectivesĪfter this session, you will be able to define low tidal volume ventilation, referred to as LTVV. This module introduces and provides evidence for the lung protective low tidal volume strategy, and offers recommendations for implementation. This has the effect of taking more oxygen into the body and removing more carbon dioxide.Slide 1: Low Tidal Volume Ventilation: Introduction, Evidence, and Implementation Minute ventilation = breathing rate × tidal volumeĭuring exercise, tidal volume increases as does the depth of breathing and the rate of breathing. The average minute ventilation is 6 litres per minute. Minute ventilation (VE) is the total volume of air entering the lungs in a minute. The average tidal volume is 0.5 litres (500 ml). Tidal volume (TV) is the amount of air breathed in with each normal breath.
The average breathing rate is 12 breaths per minute. Taking part in regular aerobic exercise has been shown to increase a person's vital capacity.īreathing rate (frequency, BR) is the number of breaths in a minute. Vital capacity is the maximum amount of air that can be breathed out after breathing in as much air as possible.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
